Using git#
QuantEcon makes use of git and github to manage changes and collaboration
for writing our Lecture series.
Branches and Pull Requests#
There are a number of benefits when using pull requests to make changes to a lecture repository.
they will generate an
htmlpreview of the lecture or changes that you are about to commitcan run additional checks like
link checkingit will confirm if a lecture has
executedon the server environment
A branch is essentially another copy of the repository that reflects another state that the repository is in. This could include changes to existing lectures or the addition of new lecture material.
It can be useful to work in a branch so that the main branch doesn’t get modified until you are ready to make the change.
Setting up a Branch#
Step 1: Always check you are up to date and center yourself around the main branch before making any changes
git checkout main
git pull
Tip
Use a terminal emulator that provides you with contextual information when inside
of git repos. For example my terminal will always show which branch I am currently
editing in, and if there are any changes to the repo.
Step 2: Create and switch to a new branch before making edits
git checkout -b solow-model
git will return some useful information once this command completes. The checkout -b is essentially short hand to both checkout and create the branch named solow-model
(quantecon) ➜ manual git:(main) ✗ git checkout -b solow-model
Switched to a new branch 'solow-model'
Step 3: Make your changes
Step 4: Commit your changes
You can commit your changes in the typical way
git add .
git commit -m "<message>"
Step 5: Push your changes to GitHub
Once you’re ready you can now push this branch to github which will activate github to prompt you to setup a pull request. Team members can review this pull request and you can review the generated html once github actions has completed executing.
git push origin solow-model
where solow-model is the name of the branch that you had created in Step 2
The output will look something like
(quantecon) ➜ manual git:(solow-model) git push origin solow-model
Enumerating objects: 7, done.
Counting objects: 100% (7/7), done.
Delta compression using up to 10 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (4/4), done.
Writing objects: 100% (5/5), 1.40 KiB | 1.40 MiB/s, done.
Total 5 (delta 2), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (2/2), completed with 2 local objects.
remote:
remote: Create a pull request for 'solow-model' on GitHub by visiting:
remote: https://github.com/QuantEcon/QuantEcon.manual/pull/new/solow-model
remote:
To https://github.com/QuantEcon/QuantEcon.manual
* [new branch] solow-model -> solow-model
Tip
If you have no more changes to make to that branch it can be a good time to
switch back to the main. Otherwise it can be easy to open terminal in the future
and start editing in an old branch
git checkout main
You can either click on the link in terminal or you can simply navigate to the repository page and github will prompt you to setup a pull request at the top of the page.
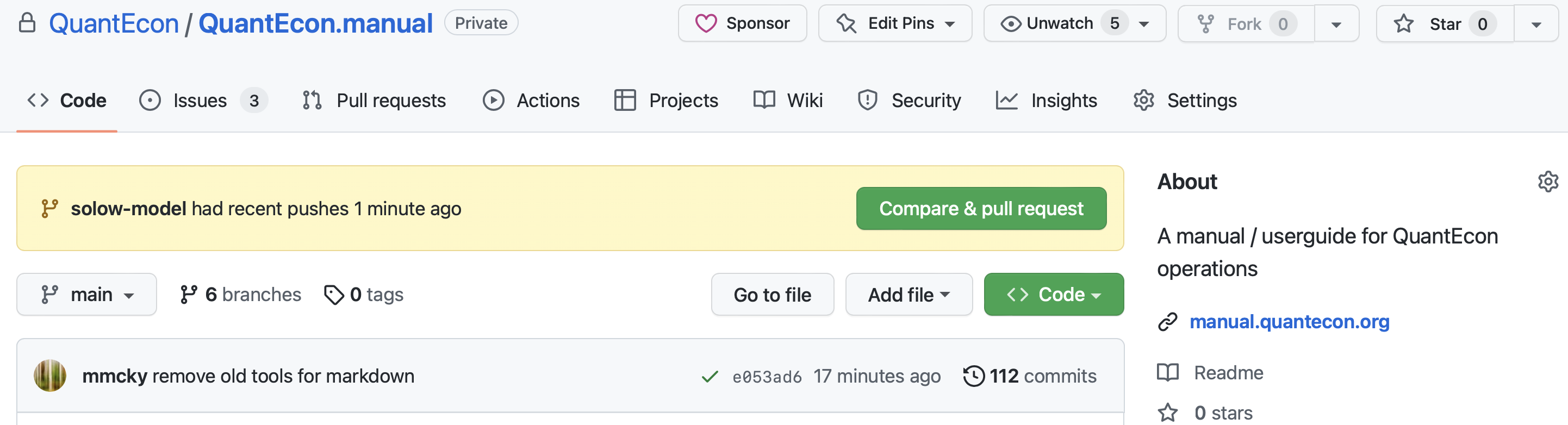
which will open a pull request
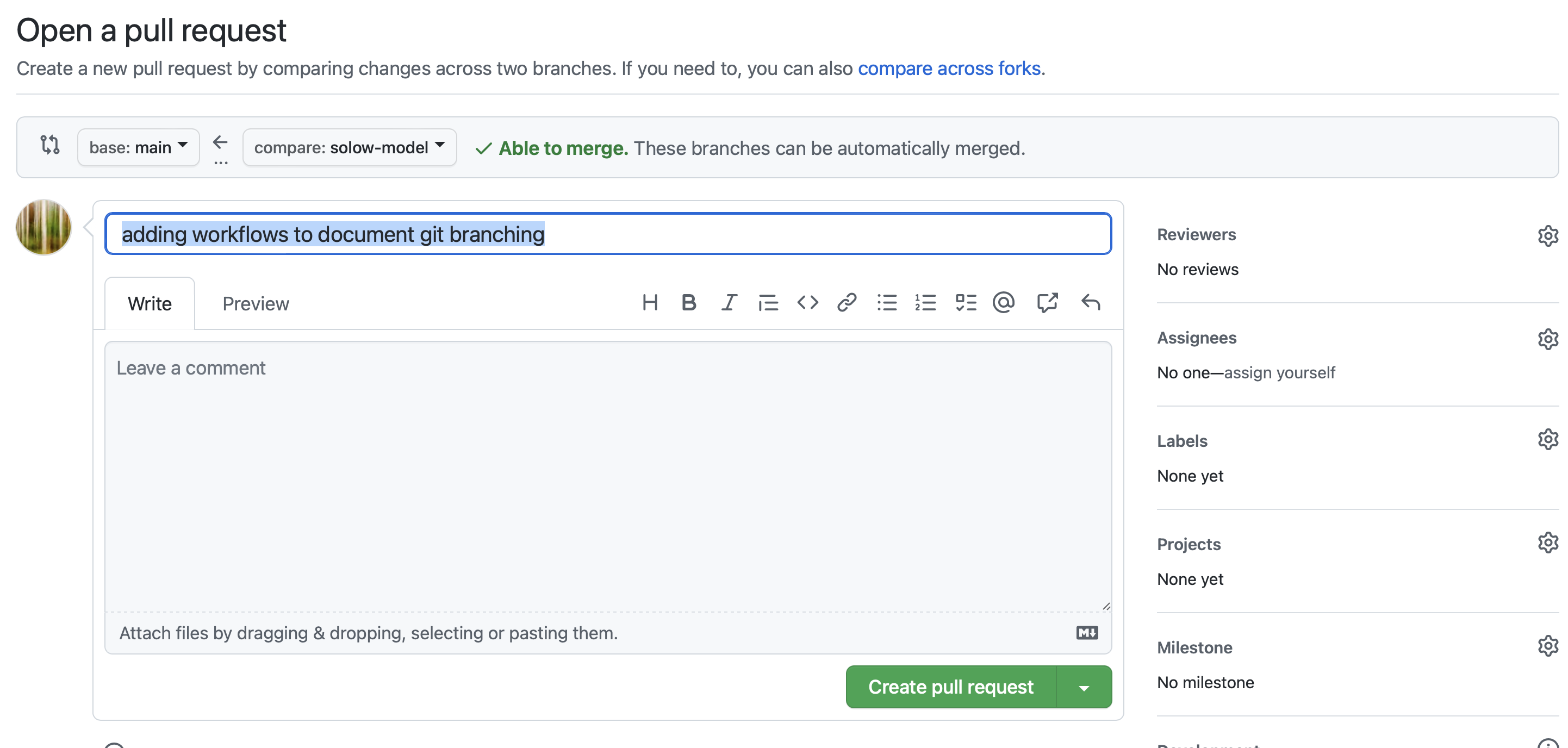
where you can add a brief description of the changes and you can alert members of the team for review.
Click on Create Pull Request when you’re done in the browser.
This will cause github actions to start building the repository and generating previews for your pull request
Note
Automatic Documentation Previews
When you create or update a pull request, GitHub Actions will automatically:
Build the documentation using Jupyter Book
Deploy a preview to
https://manual.quantecon.org/pr-{number}/Add a comment to your PR with the preview link
Update the preview whenever you push new commits
Clean up the preview when the PR is closed
This allows reviewers to see exactly how your changes will look before merging.
Step 6: Merge your Pull Request
Once everyone is happy with the pull request we can merge it into the main branch
To fetch the latest main locally you can fetch it using the standard
git pull